Your baby gets all the required nutrients from breast milk during the initial months of breastfeeding. However, things start to change when they attain the age of 6 months, their nutritional requirements increase, and complementary feeding becomes essential to fulfil the requirements.
In Sanskrit, this process is called Annaprashana, which means “initiation of food feeding” or “eating of food” without stopping the breastfeeding process. In other words, it is a much-needed concept.
6-24 months is the stage where your baby needs proper food to meet nutritional requirements that cannot be fulfilled by breastfeeding alone. It is a unique window of opportunity that prevents permanent growth from faltering in children. Hence, it is recommended that you start giving solid food to your baby during this timeline.
But before diving deep into this topic, let’s know what exactly complementary feeding is?
What Is Complementary Feeding?
Complementary feeding is the concept of starting solid food for the baby when they attain six months of age in addition to breastmilk feeds. Remember that this concept is complementary, indicating that it should complement breastfeeding. Keep in mind to include breastfeeding and to not skip it.
How? Start with feeding a small amount of food, targeting two to three tablespoons twice a day. Increase the diet according to your child’s needs. Look for signs of hunger, like when they’re putting their hand in their mouth. Stop when you see that they’re full. Do not force-feed your child.
Features Of Complementary Feeding
- Regular breastfeeding along with complementary feeding from the age of 6 months to 24 months.
- Continued breastfeeding up to 2 years of age and beyond (as per the demand).
- Follow responsive feeding, do not force feed your child.
- Prevent food-borne diseases by ensuring safe and hygienic food practices.
- Increase the frequency of feeds as the child grows and according to their nutritional requirements.
- Include a variety of foods, often mixing up different nutrient rich foods.
- Include vitamin supplements as per your child’s dietary requirements.
- Encourage fluid intake in the form of breast milk and water.
Nutrient Requirements For Children
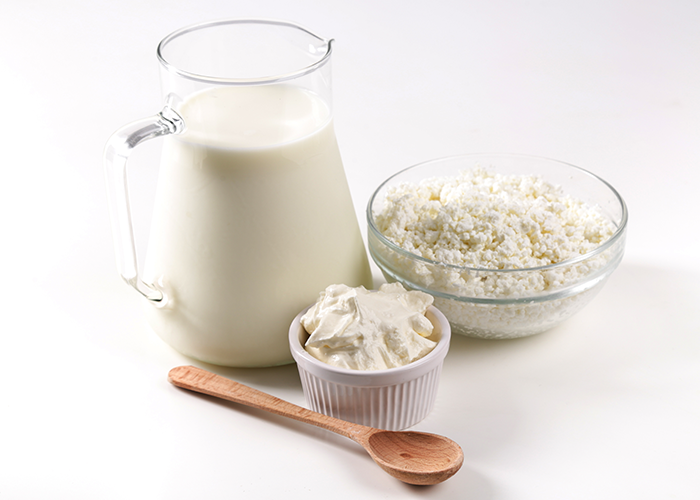

Protein sources for complementary feeding
- Proteins: Proteins are the building blocks of the human body. They help build muscles, boost the immune system, and above all, provide energy. Dairy foods like cottage cheese, curd, whole cow’s milk, pulses are good sources of proteins.
- Fats: Fats are essential for a child’s growth and contribute to their brain and nervous system development—for example, white butter, ghee, nuts, and oil seeds, etc.
- Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates provide energy to the body to run everyday functions. Good sources of carbohydrates are potatoes, beans, rice, cereal, etc.
- Vitamins & Minerals: Most important vitamins and minerals that a child needs are iron and Vitamin D. Amaranth leaves, moringa leaves, spinach, organ meats, soya beans, fortified cow’s milk, yoghurt, etc., are good sources of the same.
Tips To Keep In Mind
- Foods like whole nuts, seeds, raw vegetables, and chunks of fruits might cause choking hazards. Therefore, avoid them.
- Avoid adding sugar/salt to the food. It might cause dental problems.
- Don’t give cow’s milk directly to the baby. Instead, add it with pureed or mashed food to provide it with a smoother consistency.
- Avoid packaged food items like juice concentrates, tea, or coffee. Breast milk and water should be the only drinks to be given to your baby.
Food Ideas For Complementary Feeding
According to the CDC, a rainbow diet full of fruits and vegetables is great to start with. Here is what you can offer your child:
- Porridge, mashed vegetables and fruits
- Fruits: bananas, strawberries, melons, avocados.
- Vegetables: boiled spinach, carrots, sweet potatoes, beetroot.
- Whole grains: Legumes, whole wheat bread
- Drinks: water, breast milk.
- Others: Yogurt, pasteurized cheese, chicken, fish.
For more meal and snack ideas for your toddler, read this blog
Conclusion
Remember that nutrition during the initial years of development matters the most. Ensuring the right complementary foods along with breastfeeding can make your baby’s health foundation strong. Consequently, it ensures your child receives the required nutrients and slows down the risks of deficiencies and malnutrition.